NIST Security Measures for EO-Critical Software Use
The NIST Security Measures for EO-Critical Software Use defines critical software subject to the EO requirements, elaborates on the objectives presented in the EO and outlines security measures vendors can begin to take to meet the pending requirements.

- SM 2.3: Protect data at rest by encrypting the sensitive data used by EO-critical software and EO-critical software platforms consistent with NIST’s cryptographic standards.
- SM 2.4: Protect data in transit by using mutual authentication whenever feasible and by encrypting sensitive data communications for EO-critical software and EO-critical software platforms consistent with NIST’s cryptographic standards
- SM 3.2: Use patch management practices to maintain EO-critical software platforms and all software deployed to those platforms. Practices include:
- rapidly identify, document, and mitigate known vulnerabilities (e.g., patching, updating, upgrading software to supported version) to continuously reduce the exposure time
- monitor the platforms and software to ensure the mitigations are not removed outside of change control processes
- SM 4.2: Continuously monitor the security of EO-critical software platforms and all software running on those platforms.
Moving the U.S. Government Toward Zero Trust Cybersecurity Principles
As the Executive Order states, “The United States faces persistent and increasingly sophisticated malicious cyber campaigns that threaten the public sector, the private sector, and ultimately the American people’s security and privacy” and that “the Federal Government must take action to rapidly improve the security and integrity of the software supply chain, with a priority on addressing critical software.” To help users and their developers meet the mission, agencies are required to meet the standards and requirements released over the next year, including adopting a Zero Trust model.

OMB M-22-09 Impacts
- Devices that Federal Staff use to do their jobs are consistently tracked and monitored, and the security posture of those devices is taken into account when granting access to internal resources
- Agencies must “operate dedicated application security testing programs,”, “utilize high-quality firms specializing in application security for independent third-party evaluation,” and maintain an effective and welcoming public vulnerability disclosure program for their internet-accessible systems.”
- Applications and Workloads: Agencies treat all applications as internet-connected, routinely subjecting their applications to rigorous empirical testing, and welcome external vulnerability reports
- Analyzing software “ and its deployed functionality with a comprehensive and rigorous approach, whether their software is built internally or by a contracted vendor,” is required.
- The analysis of software is “expected to continue moving toward continuous monitoring and ongoing authorizations while employing periodic manual security assessments as applications, dependencies, components, and infrastructure evolve.”
What the Executive Order for Cybersecurity means for Mobile App Builders and Buyers
Requirements for Developers of Mobile App Software Used by Government Agencies
The new cybersecurity requirements that apply to all U.S. government federal agencies — and the software and service providers who support them — have aggressive implementation timelines, so organizations need to start acting now to ensure compliance. All mobile app developers and federal agencies using mobile apps can leverage NowSecure expertise to help secure the country and meet the requirements to avoid decommission of currently deployed software and the blocking of new purchases.

Executive Order on Improving the Nation’s Cybersecurity
The White House Executive Order for Cybersecurity lays out a number of standards and requirements to be released over the next year to protect federal agencies and the software infrastructure that runs the country. All software developers will have to comply with the Executive Order in order for agencies to continue to use their software and for them to continue selling to government agencies. Government agencies that build their own software or outsource development to systems integrators will have to comply, as well. The table below shows the requirements, where you can learn more about the Executive Order and how NowSecure can help you prepare to address them now and meet them as they are released.
Security Test Automation
Requirements
EO section 4(e)(iii) and 4(e)(iv) requires “employing automated tools, or comparable processes, to maintain trusted source code supply chains” and “employing automated tools, or comparable processes, which check for known and potential vulnerabilities and remediate them at a minimum prior to product, version, or update release.” This ties directly to Section 4(r) which defines automated tools such as SAST, DAST, IAST, SCA and API security testing and calls for penetration testing guidelines.
Resources
Building automated testing into the dev pipeline and 3rd party supply chain to identify and remediate cybersecurity vulnerabilities requires planning, expertise, tooling, integrations, and developer enablement resources. Get a jump start on this requirement today by utilizing NowSecure Platform with automated security analysis for apps built and used. Includes prebuilt SDLC integration, and embedded developer assistance.
Software Bill of Materials (SBOM)
Requirements
Section 4(e)(vii). This requires all software sellers “provide a purchaser a Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) for each product directly or by publishing it on a public website.”
Resources
Understanding all dependencies and third-party code in an application to build a SBOM is tedious, confusing, and often outdated quickly. NowSecure Platform, NowSecure Workstation and NowSecure Penetration Testing Services all provide details of SDKs, Frameworks, OSS and more in mobile apps to populate SBOM information today, to be enhanced as standards and regulations evolve.
Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) requirements were the first to be well defined and are described as a list of ingredients for an application. Simply put, an SBOM is an inventory of all the dependencies and third-party code included in an application. This includes dependencies of dependencies, known as transitive dependencies, open-source libraries, and third-party components.
Most SBOMs are generated in a machine-readable format like XML or JSON and the OWASP CycloneDX now leading standard formats. This approach inventories third-party dependencies an application has, giving agencies impetus to react quickly to remove, update, or isolate an app if a dependency is compromised.
Static, Dynamic & with Software Composition Analysis (SCA)
Requirements
Section 4(r) states that guidelines will be published for “vendors’ testing of their software code including… static and dynamic analysis, software composition tools, and penetration testing”
Resources
To meet this requirement, organizations will have to implement multiple assessment types, and disparate tools become hard to manage. NowSecure Platform includes automated static, dynamic and SCA analysis conducted on real mobile devices with over 600 tests. NowSecure Penetration Testing Services covers all static, dynamic, SCA, and penetration testing requirements.
Existing Cybersecurity Standards
Requirements
Throughout the EO, it states that the impending requirements may be “modeled after any similar existing government programs” and with rapidly approaching deadlines existing standards are likely to be leveraged
Resources
As strong advocates of standards-based testing, all NowSecure solutions implement standards including OWASP, ioXt, NIAP, and more. Leverage standards-based automated security testing with NowSecure Platform today.
NIST Security Measures for EO-Critical Software Use defines critical software subject to the EO requirements, elaborates on the objectives presented in the EO and outlines security measures vendors can begin to take to meet the pending requirements.
NIST defines critical software as “any software that has, or has direct software dependencies
New Cybersecurity Standards
Requirements
The EO puts forward a timeline for new, comprehensive standards and regulations for cybersecurity that have a wide breadth according to the timelines noted including 14034
Resources
Executive Order 14034
Tangentially related to the original Cybersecurity EO, the White House also published Executive Order 14034 on “Protecting Americans’ Sensitive Data From Foreign Adversaries.”
This EO details the security threat of applications which run on “personal electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, and computers” and their ability to capture “vast swaths of information from users, including United States persons’ personal information and proprietary organization information.”
14034 describes mobile application cybersecurity attacks as “an unusual and extraordinary threat to the national security, foreign policy, and economy of the United States.”
The EO on Protecting Sensitive Data defines the indicators of risk and the sensitive data at risk to foreign adversaries and introduced a second set of deadlines that are available on the NowSecure Cybersecurity Executive Orders page.
Cybersecurity Consumer Labels
Requirements
Sections 4(t) and 4(u) require the creation of “IoT cybersecurity criteria for a consumer labeling program” and a broader “consumer labeling program” that software vendors will be subject to.
Resources
The labeling programs outlined in the EO will apply to all software developers and IoT manufacturers to provide consumers with an understanding of the level of security that has been applied to a product, even if that software is not sold to the Federal Government. NowSecure can help organizations get ahead of the requirements that exist today and the compliance requirements coming from the EO to be prepared for the release of the cybersecurity labels with a suite of Mobile AST Solutions, training services, and more
Proof of Compliance
Requirements
Vendors will need to provide Proof of Compliance with the Sections 4(e)(ii) Secure Software Development, 4(e)(v) Automated Vulnerability Scanning, 4(e)(ix) Attesting to Secure Development and 4(e)(x) Attesting to Software Integrity for continuous organization with government agencies. The FAR Council will define the contract language requiring this proof.
Resources
Implementing the testing required to meet the requirements of the EO may seem cumbersome, but once the FAR Council has published the contract language it will be required across all agencies. NowSecure can not only provide the testing software that the EO requires, but it can also produce proof of compliance. This is critical as, once the agencies have adopted the language from the FAR Council, failure to comply with it will result in the removal of software and the blocking of future purchases according to Section 4(p).
Office of Management and Budget (OMB)
Requirements
OMB M-21-30, “Protecting Critical Software Through Enhanced Security Measures” doubles down on the importance of securing the critical software as defined by NIST. This OMB EO defines the early phases of the approach being taken by the government to secure the apps they are building and help fix the “software is commercially developed through an often-opaque process often lacking sufficient controls to prevent the creation and exploitation of significant application security vulnerabilities.”
Phase 1 of the EO rollout criteria applies to identity, credential, and access management (ICAM) software, operating systems, hypervisors, container environments, web browsers, endpoint security, network control, network protection, network monitoring and configuration, operational monitoring and analysis, remote scanning, remote access and configuration management, and backup/recovery and remote storage software.
Phase 2 expands to software that controls access to data, cloud-based and hybrid software, software development tools, such as code repository systems, testing software, integration software, packaging software, and deployment software, software components in boot-level firmware, and software components in operational technology (OT).
OMB M-21-31 & M-22-01
OMB M-21-31 on “Improving the Federal Government’s Investigative and Remediation Capabilities Related to Cybersecurity Incidents” and OMB M-22-01 on “Improving Detection of Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities and Incidents on Federal Government Systems through Endpoint Detection and Response” both expanded the scope of the EO-impacted software to include software in the Enterprise Mobility Management, Unified Endpoint Management, Mobile Threat Defense, Mobile Device Management, International Mobile Equipment Identity and International Mobile Subscriber Identity categories, and by stressing mobile phones as a critical endpoint for EDR solutions insight.
Resources
Using the NowSecure platform pinpoints OMB gaps including weak or non-existent authentication. Without NowSecure applications may grant an attacker unauthorized access to an app. The platform helps developers require, if not at least support, complex passwords, including length of at least six alphanumeric characters (more characters is always stronger). Requiring the selection of a secret word or icon (which the user does not create themselves) as part of the log-in process can help protect users’ accounts in the event they re-use passwords and their password was exposed as part of another data compromise.
FISMA Reform Act
Requirements
FISMA Reform Act offers massive implications for mobile app security practitioners and mobile app developers requiring agencies to “evaluate mobile application security guidance and issue guidance to secure mobile devices, including for mobile applications, for every agency” in less than one year.
For government agencies, this will also require continuous inventory of all “mobile devices operated by or on behalf of the agency; and vulnerability identified by the agency associated with a mobile device” and require every agency to perform continuous “evaluation of vulnerabilities and other risks associated with the use of applications on mobile devices.”
Resources
NowSecure integrates with most popular EMM/MDM platforms to help in modernizing Federal information security management while improving Federal cybersecurity for mobile users to combat persisting and emerging threats, and for other purposes
Requirements for government Agencies Acquiring Mobile App Software
Understand the Requirements for Mobile App software
Understand the Requirements for Mobile App Software
As the Executive Order states, “The United States faces persistent and increasingly sophisticated malicious cyber campaigns that threaten the public sector, the private sector, and ultimately the American people’s security and privacy” and that “the Federal Government must take action to rapidly improve the security and integrity of the software supply chain, with a priority on addressing critical software.” To help users and their developers meet the mission, agencies are required to meet the standards and requirements released over the next year.

Address Executive Order Requirements with NowSecure
NowSecure helps agencies immediately address many of the requirements from Zero Trust to Internet of Things, and Application Supply Chain Security to Automated Testing to Continuous Diagnostic Mitigations. The table below shows the Executive Order requirements and how NowSecure can help you address them now and in the future.
Zero Trust
Requirements
Two areas from differing agencies: OMB M-22-09 on “Moving the U.S. Government Toward Zero Trust Cybersecurity Principles” and NIST Section 3(b)(ii) Zero Trust Architecture” per the Department of Commerce
Government’s efforts to a Zero Trust Architecture have major implications for mobile apps. One proposed strategy entails consistently tracking and monitoring the security posture of the mobile devices used by federal staff, and using the security posture to make decisions when granting access to internal resources.
Individuals using a mobile application with subpar security may be blocked from accessing critical information. Zero Trust efforts are improved through establishing a public vulnerability disclosure program for government agencies to work directly with security researchers.
Resources
Zero Trust applies to both mobile devices and mobile apps, whether BYOD or agency owned. NowSecure Platform for Mobile App Vetting continuously monitors public app stores for vulnerabilities and risks in third-party apps.
Integrated with EMM/MDM platforms, NowSecure proactively identifies risky apps to prevent deployment and alerts when existing mobile app updates expose new vulnerabilities. This also applies to the FISMA reform act noted above.
Internet of Things (IoT) Apps and Devices
Requirements
More than 38 billion internet of things (IoT) connected devices worldwide exist today growing to 75 million by 2025. To instill every user’s confidence in IoT apps, the ioXt Alliance has created a certification to ensure a secured interface for buyers, end-users, and channel partners.
Section 4(t) requires “identify IoT cybersecurity criteria for a consumer labeling program” and may consider “a consumer labeling program may be operated in conjunction with or modeled after any similar existing government programs”.
Resources
As a member of the ioXt Alliance, NowSecure is an ioXt Authorized Lab that co-authored the IoT-connected mobile app security standards. NowSecure provides fast turnaround, high-quality results, and collaborative assistance to quickly complete ioXt compliance certification. With this experience, NowSecure is well equipped to help agencies solve for the upcoming IoT compliance requirements.
Application Supply Chain
Requirements
All the security requirements for Software Sellers are mirrored onto the government agency. Agencies will be expected to require automated security testing, a software bill of materials, software composition analysis, and compliance with standards established for all software purchases and use.
Resources
Supply chain mobile app risks impact sourcing, vendor management, partner continuity and quality, transportation security. To proactively protect supply chain organizationes, leverage an always-growing database of NowSecure Platform data. NowSecure’s Privacy and Breach tracker is a subset of this data that is publicly available to help raise awareness and educate on the risks prevalent in mobile apps by agency focus area.
Continuous Diagnostic and Mitigation (CDM) Program
Requirements
Section 7(f) mandates that agencies must establish or update a Memoranda of Agreement (MOA) with CISA for the CDM Program.
Resources
Preventing and protecting mobile app incidents is a core component of any CDM program. NowSecure Platform continuously monitors all mobile apps — internally or externally developed — to proactively identify cybersecurity issues and aid in mitigating those issues to protect the agency.
Data Logging
Requirements
Section 8(b) and (e): require the creation, production, and protection of logs that, upon request, are provided “to the Secretary of Homeland Security through the Director of CISA and to the FBI”
Resources
Tracking and reporting on cyber risk and incidents requires an objective, third-party perspective. NowSecure can proactively track these for mobile apps and devices and can help agencies maintain and deliver their logs in a way that is compliant with the EO requirements.
NowSecure currently has software installed in the government customer environment that can produce this information for Homeland Security and the FBI.
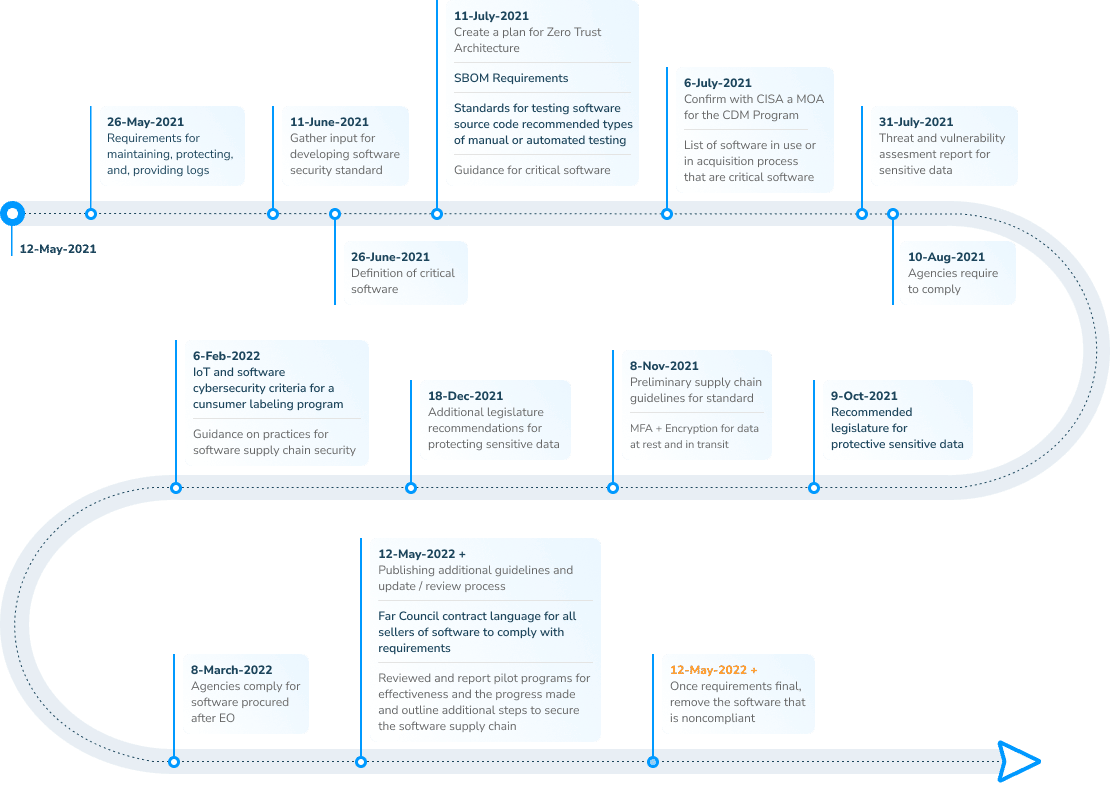
When Are the Requirements from the Executive Order Being Released?
The White House Executive Order provides a complicated rolling schedule of criteria and activities to be completed. NowSecure analyzed and documented key mobile app security aspects of the Executive Order helping stakeholders rapidly identify the relevant issues. Leverage this timeline for your planning and keep it handy as we update it in the future.

What the Executive Order on Protecting Sensitive Data Means for Mobile Apps
The Security Threat of Applications Which Run on “Persona Electronic Devices”
A second Executive Order details the security threat of applications which run on “personal electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, and computers” and the ability they have to capture “vast swaths of information from users, including United States persons’ personal information and proprietary organization information.” Cybersecurity attacks are classified in this Executive Order as “an unusual and extraordinary threat to the national security, foreign policy, and economy of the United States.” Applications which meet any of the criteria defined in the Executive Order below are at risk of legislative actions within the next year. Detailed deadlines created by this Executive Order have been included in the updated timeline graphic above. NowSecure can help organizations get a jump start on building compliant applications and identifying applications they use that are noncompliant today.
Indicators of Risk
- Ownership, control, or management supported by a foreign adversary
- Use of the application to conduct surveillance that enables espionage
- Ownership, control, or management subject to coercion by a foreign adversary
- Ownership, control, or management involved in malicious cyber activities
- A lack of thorough and reliable third-party auditing
- The scope and sensitivity of the data collected
- The number and sensitivity of the users of the connected software application
- The extent to which risks have been or can be addressed

Apps that Contain Sensitive Data are Valuable Targets
Apps that participate in the unrestricted sale, transfer, or access of:
- Personally identifiable information
- Personal health information
- Genetic information
- Large data repositories by persons owned or controlled by, or subject to the authority or direction of, a foreign adversary.

NowSecure Powers Federal Agency Success
U.S. Department of Justice
The Justice Management Division pairs NowSecure Platform with mobile device management to automatically security test and blacklist risky apps in the supply chain and uses NowSecure Workstation to deeply test sensitive mobile apps.
U.S. Air Force
The Platform One factory integrates NowSecure Platform within the CI/CD pipeline to automatically test the security of DoD apps as airmen build them.
U.S. Air Force
The BESPIN team partners with NowSecure to train developers on secure coding, automate security testing of mobile apps in the CI/CD pipeline and assess apps for NIAP standard compliance.
U.S Department of Homeland Security
The AppVet program includes NowSecure Platform to quickly assess the security and supply-chain risk of mobile apps used throughout the U.S. government.



